EarSketch
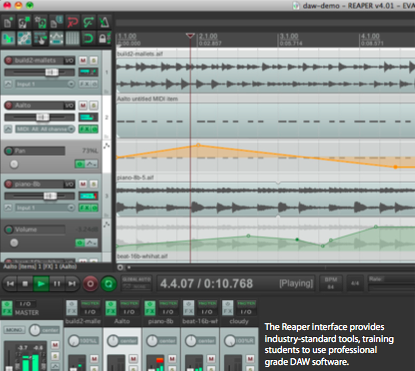
Computational remixing of hip hop (i.e. using code to control loops and beats to compose music) can be used as a tool for the cultural engagement in computing of underrepresented populations. EarSketch is a digital audio workstation environment, with an accompanying curriculum, that will allow high school and summer workshop students to create their own computational remixes through learning computing principles.
LuminAI
Computational Play
Adaptive Games
Digital Improv
This project explores how to formalize techniques used in real-world interactive drama domains (e.g. tabletop role-playing, improvisational theatre, and live action role-play). Such formalizations can better inform our design of story directors and synthetic characters for digital interactive drama systems.
Drawing Apprentice
With the Drawing Apprentice, we explore how computers can co-create with humans in abstract art.The Drawing Apprentice is an enactive AI drawing partner. It is ‘enactive’ in the sense that its contributions are improvisational and based on the sketch input of the user. There is a reciprocal feedback loop between the user and the system.
Virtual Coach for Medical Training
ISAT
Scribe